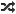Trace
Wavepoint provides several ways to trace the fiber network. You can trace fiber connectivity, with or without a designated circuit. You can run Full Path and OTDR traces from ports and splice points. Further, you can run a trace through a splitter, and you have the opportunity to direct the trace path on the input or output side of the splitter. All traces provide summary details of the results and a one-line diagram of the trace path. Finally, all this information can be printed, including the diagrams.
Fiber Connectivity and Circuit Trace
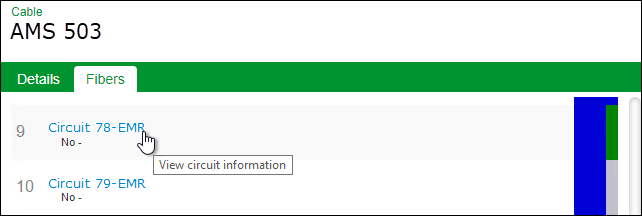
- Locate the desired fiber optic cable, then click the Fibers tab.
- Scroll to locate the desired fiber.
- If a circuit is present, click the Circuit name to initiate the trace.
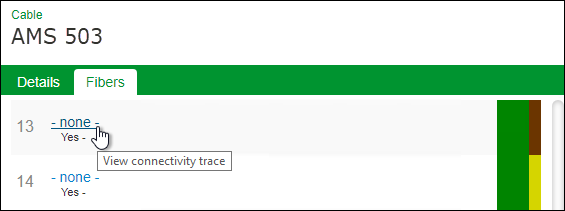
- If no circuit is present, click the name “none” to initiate the trace.
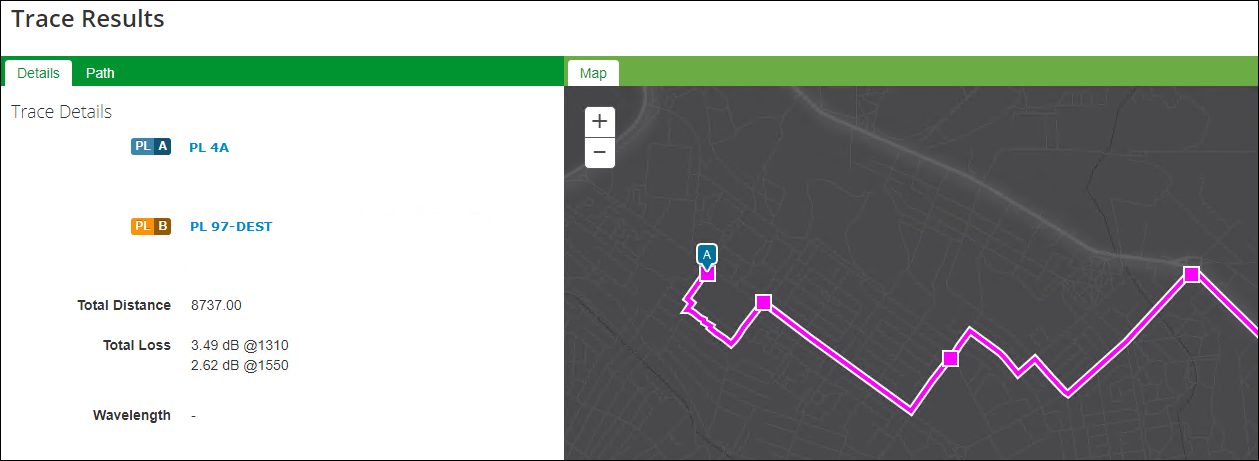
- The Details tab provides summary information of the trace:
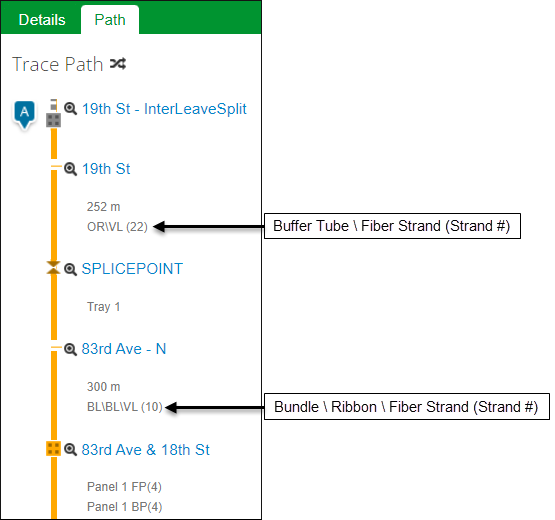
- The Path tab provides a one-line diagram of the trace.
- Click any cable or facility name along the path to see more information about that component.
Full Path Trace from a Port
- Locate the desired rack, device, or splitter.
- On the Ports tab, locate the desired port and click it.
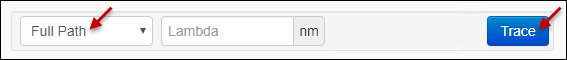
- On the left-hand side, specify Full Path and optionally a specific wavelength, then click Trace.
- Much like the Fiber Connectivity trace, the Details tab provides summary information, and the Path tab provides a one-line diagram of the trace results.
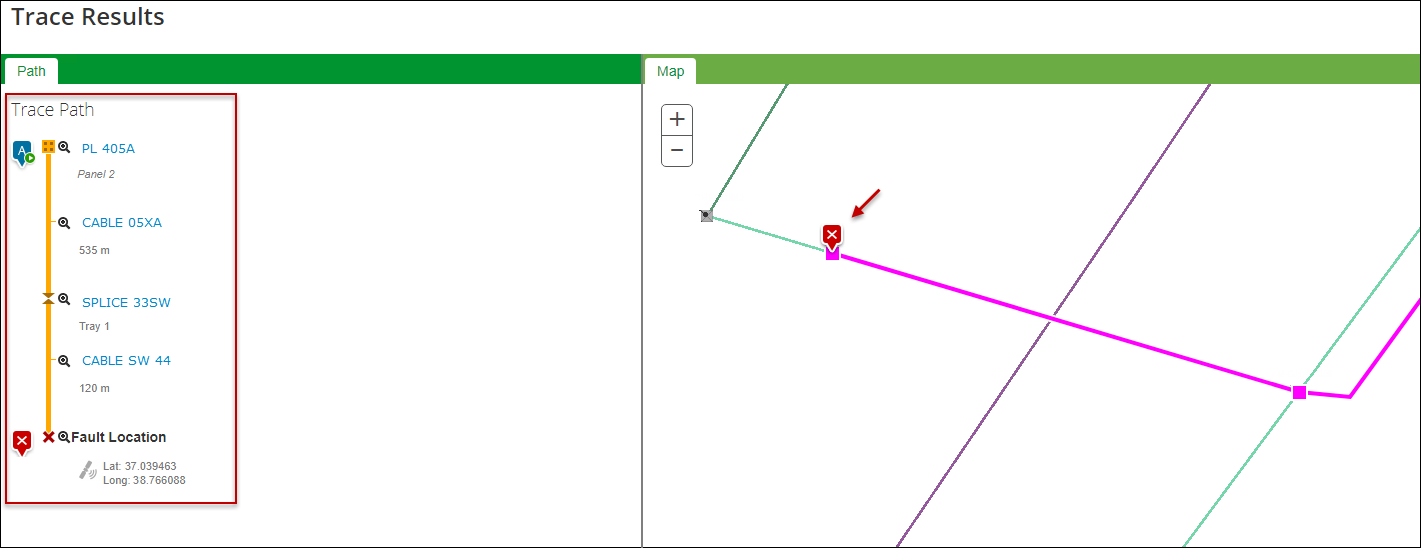
OTDR Trace
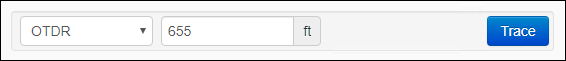
- After locating and clicking your desired port or fiber strand (if starting the trace from within a splice point), change the trace type to OTDR.
- Type in the distance provided by the reflectometer, then click Trace.
- The application provides a one-line diagram up to the distance provided.
- Further, it displays the fault location at the end of the diagram and on the map.
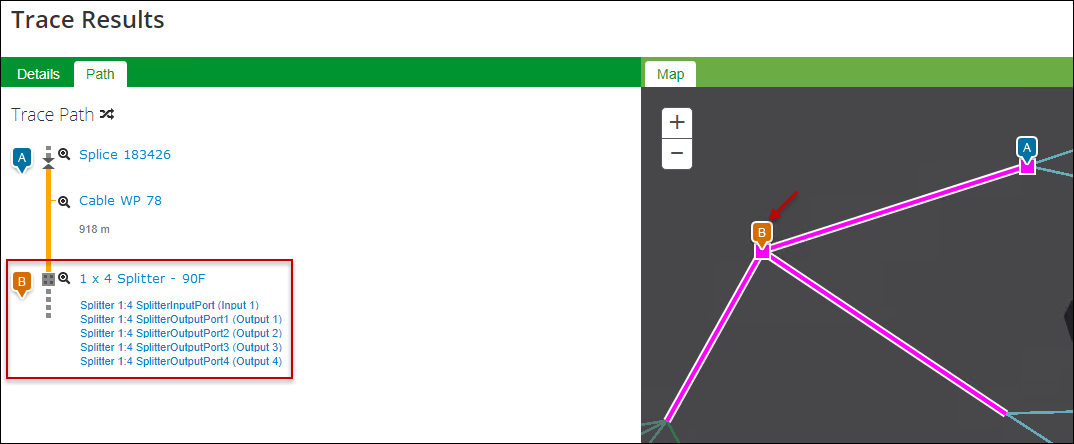
Trace through a Splitter
- Locate and click the desired port or fiber to initiate the trace.
- When the trace encounters a splitter, it pauses the trace and displays the splitter in both the one-line diagram and on the map. Further, it displays the possible input and output ports on the diagram and their immediate cable connections on the map. For example, in this image, notice the trace has temporarily stopped at a 1 x 4 splitter, and there are two possible paths (on the map) from that device.
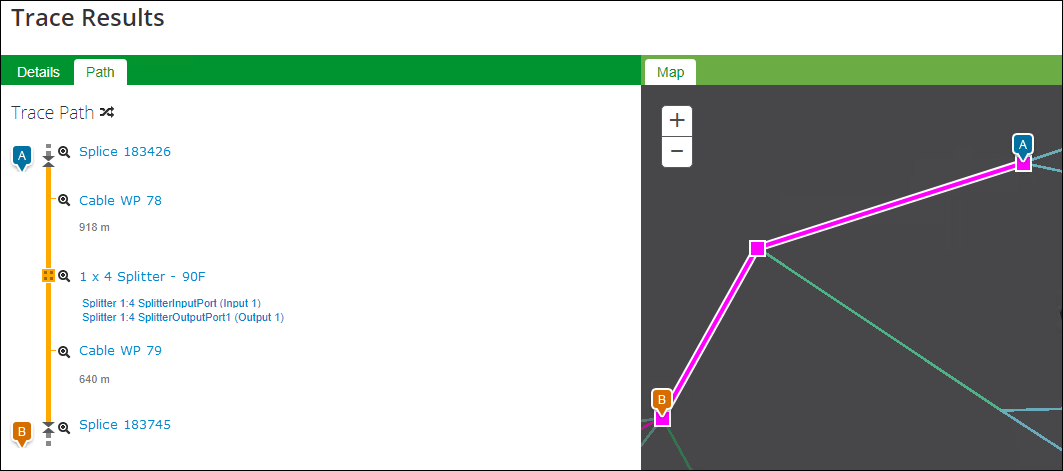
- To continue the trace, click the desired input or output port. For example, in the following image output port 1 was chosen, and the trace continued along that path.