Tap-Linked Distributed Modbus Architecture
Introduction
The tap-linked distributed Modbus architecture can be one of the following:
-
A Modbusspitter block distributes Modbuscable-up to eight IFM interfaces.
-
The main segment of the Modbus cable has a shunt terminal block on the incomer of each cubicle and the IFM interfaces are connected on a tap link cable.
Tap-Linked Distributed Modbus Architecture With Modbus Splitter Block
The following figure shows an example of a tap-linked distributed Modbus architecture with nine IMUs:
-
An IMU consisting of a ComPacT NS circuit breaker and an IFM interface.
-
Eight IMUs consisting of a ComPacT NSX circuit breaker, an IFM interface, and an FDM121 display each.
|
A |
24 Vdc AD power supply for MicroLogic trip units in MasterPact NT/NW or ComPacT NS circuit breakers |
|
B |
Modbus splitter box |
|
C |
Modbus line termination |
|
D |
24 Vdc ABL8 power supply for ULP modules |
|
E |
NSX cord |
|
F |
RJ45 plug/plug ULP cord |
|
G |
IFM interface |
Tap-Linked Distributed Modbus Architecture With Modbus T-junctions
The following figure shows an example of a tap-linked distributed Modbus architecture with ten IMUs:
-
An IMU consisting of a ComPacT NS circuit breaker and an IFM interface.
-
Nine IMUs consisting of a ComPacT NSX circuit breaker, an IFM interface, and an FDM121 display each.
|
A |
24 Vdc AD power supply for MicroLogic trip units in MasterPact NT/NW or ComPacT NS circuit breakers |
|
B |
Shunt terminal block on the incoming supply |
|
C |
24 Vdc ABL8 power supply for ULP modules |
|
D |
NSX cord |
|
E |
RJ45 plug/plug ULP cord |
|
F |
RJ45 Modbus T-junction |
|
G |
Shunt terminal block on the cubicle incomer |
|
H |
Modbus line termination |
|
I |
Modbus cable running to the second cubicle |
|
J |
IFM interface |
|
K |
Modbus cable running to the third cubicle |
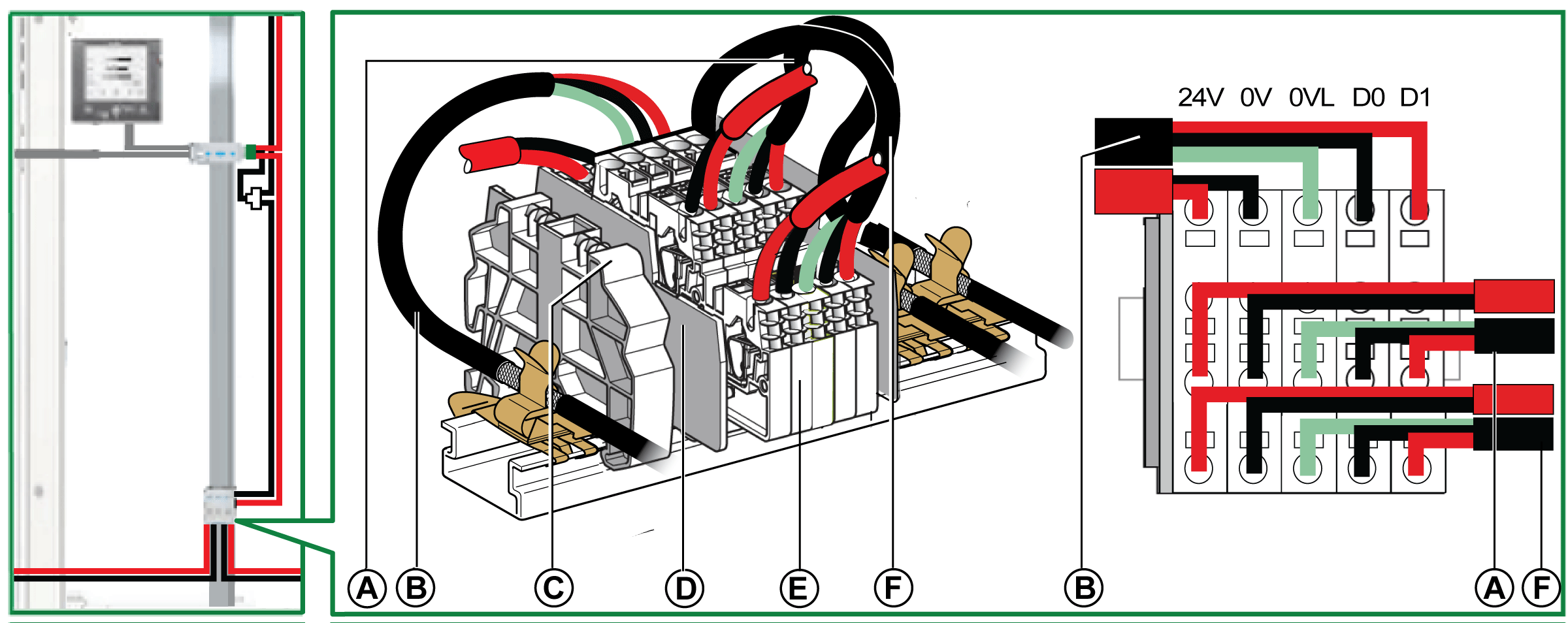
Shunt Terminal Block on the Incoming Supply
The shunt terminal block on the incoming supply can be used to connect the Modbus cable and the power supply for all the IMUs.
The shunt terminal block consists of four 4-channel spring terminal blocks and one functional ground terminal block offering grounding of the Modbus cable shielding by connection to the DIN rail.
|
A |
24 Vdc power supply |
|
B |
Modbus cable coming from Modbus client |
|
C |
Clip-on plastic end stop |
|
D |
End plate |
|
E |
Spring terminal block |
|
F |
Modbus cable running to first cubicle |
The following table lists the part numbers for the shunt terminal block:
|
Component |
Nominal cross-section |
Part number |
|---|---|---|
|
4-channel spring terminal block |
2.5 mm2 (14 AWG) |
NSYTRR24D+NSYTRALV24 (gray) |
|
End plate |
– |
AB1 RRNACE244 |
|
Clip-on plastic end stop |
– |
AB1 AB8R35 |
Modbus Cable Connection
-
The Modbus cable coming from the Modbus client ensures continuity of the Modbus signal (D0, D1, and 0 VL) and shield continuity by using brass clamps. The brass clamps must have suitable diameter for the cable type and fixings compatible with the installation (for example, screw or DIN rail).
-
The Modbus cable running to the first cubicle ensures continuity of the Modbus signal (D0, D1, and 0 VL) and shield continuity by using brass clamps. The brass clamps must have suitable diameter for the cable type and fixings compatible with the installation (for example, screw or DIN rail) for the cubicle.
The 24 Vdc power supply running to the first cubicle ensures continuity of the power supply.
-
The unused channel on the shunt terminal block can be used to connect another Modbus server in the electrical equipment (a PM800 communicating power meter, for example).
Wiring Diagram of Shunt Terminal Block on the Incoming Supply
|
A |
24 Vdc power supply |
|
B |
Modbus cable coming from Modbus client |
|
C |
Modbus cable running to first cubicle |
|
D |
24 Vdc power supply cable running to first cubicle |
|
E |
Modbus server (for example, MasterPact NT/NW circuit breaker) |
Shunt Terminal Block on the Cubicle Incomer
The shunt terminal block on the cubicle incomer distributes the Modbus signal and the 24 Vdc power supply to the cubicles in the electrical equipment.
The shunt terminal block is created using four 5-channel spring terminal blocks.
|
A |
Modbus cable rising up the cubicle |
|
B |
Upstream Modbus cable |
|
C |
Clip-on plastic end stop |
|
D |
End plate |
|
E |
Spring terminal block |
|
F |
Downstream Modbus cable |
Wiring Diagram of Shunt Terminal Block on the Cubicle Incomer
|
A |
Upstream Modbus cable |
|
B |
Upstream 24 Vdc power supply cable |
|
C |
Modbus cable rising up the cubicle |
|
D |
24 Vdc power supply cable rising up the cubicle |
|
E |
Downstream Modbus cable |
|
F |
Downstream 24 Vdc power supply cable |
Case of Several Power Supply Segments
When more than one 24 Vdc power supply is needed (refer to segmented power supply), then several power supply segments are used along the Modbus cable.
|
A |
24 Vdc AD power supply for MicroLogic trip units in MasterPact NT/NW or ComPacT NS circuit breakers |
|
B |
Shunt terminal block on the incoming supply |
|
C |
24 Vdc ABL8 power supply for ULP modules |
|
D |
Modbus cable running to the first cubicle |
|
E |
NSX cord |
|
F |
RJ45 Modbus T-junction |
|
G |
Shunt terminal block on the incomer of the first cubicle |
|
H |
Modbus line termination |
|
I |
Modbus cable running to the second cubicle |
|
J |
IFM interface |
|
K |
Shunt terminal block on the incomer of the second cubicle |
|
L |
Modbus cable running to the third cubicle |
|
M |
Shunt terminal block on the incomer of the third cubicle |
Shunt Terminal Block on the Incomer of the Second Cubicle
The shunt terminal block on the incomer of the second cubicle is created using four 4-channel spring terminal blocks and one functional ground terminal block offering grounding of the Modbus cable shielding by connection to the DIN rail.
For the shunt terminal block part numbers, refer to the appropriate component.
|
A |
Modbus cable rising up the second cubicle |
|
B |
Modbus cable coming from the first cubicle |
|
C |
Clip-on plastic end stop |
|
D |
End plate |
|
E |
Spring terminal block |
|
F |
Modbus cable running to the third cubicle |
Modbus Cable Connection
-
The Modbus cable coming from the shunt terminal block on the incomer of the first cubicle ensures continuity of the Modbus signal (D0, D1, and 0 VL) and shield continuity by using brass clamps. The brass clamps must have suitable diameter for the cable type and fixings compatible with the installation (for example, screw or DIN rail) for the second cubicle.
The 24 Vdc power supply coming from the shunt terminal block on the incomer of the first cubicle ensures continuity of the power supply for the second cubicle.
-
The Modbus cable running to the third cubicle ensures continuity of the Modbus signal (D0, D1, and 0 VL) and shield continuity by using brass clamps. The brass clamps must have suitable diameter for the cable type and fixings compatible with the installation (for example, screw or DIN rail).
The 24 Vdc power supply running to the third cubicle ensures continuity of the power supply.
Wiring Diagram of Shunt Terminal Block on the Incomer of the Second Cubicle
|
A |
Modbus cable coming from first cubicle |
|
B |
24 Vdc power supply cable coming from first cubicle |
|
C |
Modbus cable rising up second cubicle |
|
D |
24 Vdc power supply cable rising up second cubicle |
|
E |
Modbus cable running to third cubicle |
|
F |
24 Vdc power supply cable running to third cubicle |
Shunt Terminal Block on the Incomer of the Third Cubicle
The shunt terminal block on the incomer of the third cubicle can be used to connect a new 24 Vdc power supply to power the IMUs in the third cubicle.
The shunt terminal block is created using four 4-channel spring terminal blocks and one functional ground terminal block offering grounding of the Modbus cable shielding by connection to the DIN rail.
|
A |
24 Vdc power supply |
|
B |
Modbus cable coming from the shunt terminal block on the incomer of the second cubicle |
|
C |
Clip-on plastic end stop |
|
D |
End plate |
|
E |
Spring terminal block |
|
F |
Modbus cable rising up the third cubicle |
Modbus Cable Connection
-
The Modbus cable coming from the shunt terminal block on the incomer of the second cubicle ensures continuity of the Modbus signal (D0, D1, and 0 VL) and shield continuity by using brass clamps. The brass clamps must have suitable diameter for the cable type and fixings compatible with the installation (for example, screw or DIN rail).
-
The Modbus cable rising up the third cubicle ensures continuity of the Modbus signal (D0, D1, and 0 VL) and shield continuity by using brass clamps. The brass clamps must have suitable diameter for the cable type and fixings compatible with the installation (for example, screw or DIN rail) for the third cubicle.
The 24 Vdc power supply rising up the third cubicle ensures continuity of the power supply for the third cubicle.
Wiring Diagram of Shunt Terminal Block on the Incomer of the Third Cubicle
|
A |
24 Vdc power supply |
|
B |
Modbus cable coming from second cubicle |
|
C |
Modbus cable rising up third cubicle |
|
D |
24 Vdc power supply cable rising up third cubicle |